Cookies are not enabled on your browser.
Cookies are not enabled on your browser.Cookies are required for our site. Please enable cookies in your browser preferences to continue.
- Barcode / RFID / Vision
- Bulk Wire & Cable
- Cables (Terminated)
- Circuit Protection / Fuses / Disconnects
- Communications
- Drives & Soft Starters
- Enclosure Thermal Management & Lights
- Enclosures & Racks
- Field I/O
- HMI (Human Machine Interface)
- Hydraulic Components
- Motion Control
- Motor Controls
- Motors
- Pneumatic Components
- Power Products (Electrical)
- Power Transmission (Mechanical)
- Process Control & Measurement
- Programmable Controllers
- Pushbuttons / Switches / Indicators
- Relays / Timers
- Safety
- Sensors / Encoders
- Stacklights
- Structural Frames / Rails
- Tools & Test Equipment
- Valves
- Water (Potable) Components
- Wire & Cable Management
- Wire & Cable Termination
- Retired Products
Configuration Utilities
- PLC Family Selector
- P1000 PLC Systems
- P2000 PLC Systems
- P3000 PLC Systems
- ProductivityCODESYS
- CLICK PLC Systems
- Do-more® BRX PLC Systems
- LS-Electric® XGB PLC Systems
- Productivity®Open Systems
- Datalogic® Safety Light Curtains
- LS-Electric® Servo Systems
- Nitra® Pneumatic Grippers
- Object Detection (Sensors)
- PAL Controller Configurator
- Precision Gearbox Selector
- Protos X® Field I/O
- Pyrometers Selector
- Quadritalia® Modular Enclosures
- Stellar® Soft Starters
- Stepper System Selector
- SureFrame T-slot Extrusion
- SureMotion® XYZ Gantry
- SureServo2® System Selector
- SureStep® Linear Actuators
- Timing Belts & Pulleys
- Werma® Stacklights
- ZIPLinks
Tubing and Hoses
In modern pneumatic systems, most designers use flexible tubing or hose rather than rigid tubing, and many different types are available.
Tubing
Tubing is typically a simple extrusion of nylon, polyurethane(PUR), or sometimes a specialty material such as PTFE. Most tubing used in pneumatic systems is less than 1” OD with common pneumatic main supply circuits in the 1/4” to 1/2” tube OD range, and pneumatic control circuits in the 1/8” to 3/8” tube OD range. Coiled and "bonded" varieties are available in most sizes. Tubing is typically specified based on it's Outside Diameter (OD) in order to simplify matching the tubing to the "push lock" or other fitting that will be used.
Hose
Hoses are typically sold with rigid or swivel fittings attached at the ends, and sometimes have a nylon braid between the inner and outer layers for added strength. Whether the hose is rubber or lighter weight polyurethane or other materials, it’s strong, flexible and kink resistant, and thus an easy way to connect shop air to blow guns or other pneumatic tools. Hoses are commonly available in 1/4”, 3/8” and ½” diameters with national pipe thread (NPT) or quick disconnect fittings (QD). Hose is normally specified by it's Inner Diameter (ID).
Choose 'diameter' carefully
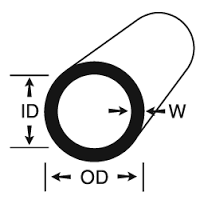
Tip: Specify tubing using OD,
Specify hoses using ID

NITRA Tubing and Hoses
Selecting the Right Material
There are a variety of materials used to make pneumatic tubing & hose including:
- Polyurethane
- PVC
- Nylon
- Polyethylene
- PTFE
Polyurethane is strong, flexible and has excellent kink resistance compared to other material types. It has a working pressure of 150 psi or higher and is the most commonly used tubing/hose material. It also has tight OD tolerance, and a wide range of push-to-connect fittings are available. A variety of colors and diameters are offered to help identify pneumatic circuits, and UV stabilization is an option for outdoor use.
Polyurethane and PVC tubing are the most flexible of the materials listed above. Polyurethane is very durable with outstanding memory, making it a good choice for coiled, portable or self-storing pneumatic hose applications. PVC is not as tough as polyurethane, but can be specified for food-grade applications, and is a good choice when high flexibility and low cost are required.
Nylon and polyethylene are harder plastics and are less flexible, making them good choices for air distribution and straight run piping applications. Notable advantages of nylon are its higher working pressure capability (up to 800 psi), temperature range up to 200°F, and excellent chemical resistance.
PTFE tubing has several notable properties including high heat resistance, excellent chemical resistance, and good dielectric properties. PTFE tubing can handle temperatures up to 500°F, is chemically inert, and can be used in applications sensitive to static electricity.
Shop for NITRA® Tubing and Hose
Check out our job openings
Free Online PLC Training
FREE Video Tutorials
FREE e-Newsletter
Automation Notebook
Product Literature
White Papers
News, Product and Training Bulletins
E-Books
 Safe &
Secure
Safe &
Secure

We accept VISA, MasterCard, Discover, American Express, PayPal or company purchase orders.
Voted #1 mid-sized employer in Atlanta
Check out our
job openings

 Loading...
Loading...